
Right Now
06:41Rise & Set
Sky Position
Top-down view📅 Upcoming Phases



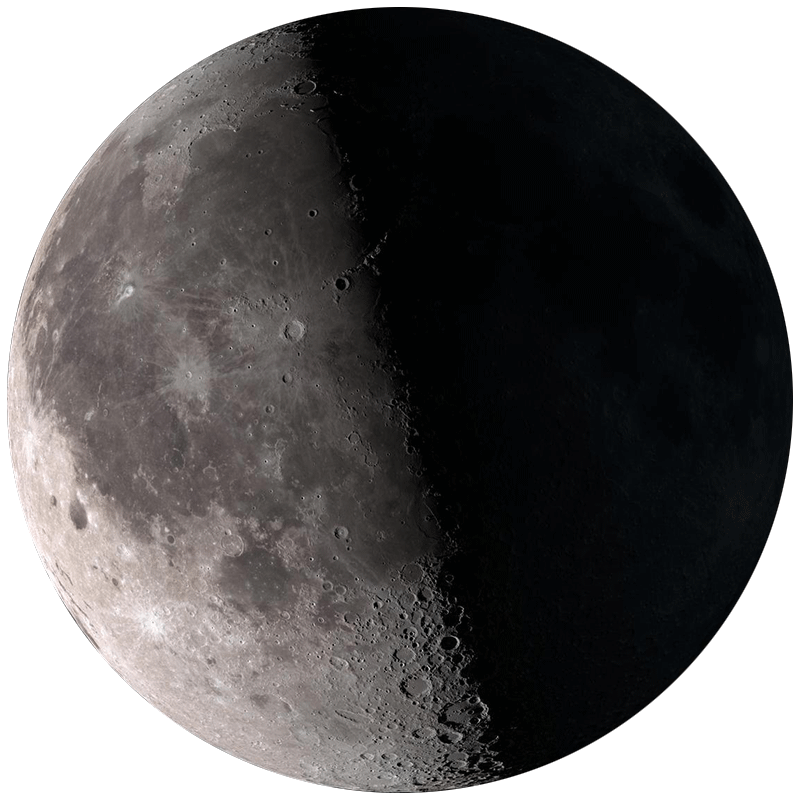
📖 Moon Phase Reference Guide
The Moon goes through 8 distinct phases during its 29.5-day cycle. Understanding these phases helps plan your stargazing sessions.

The Moon is between Earth and Sun. Invisible from Earth. Best time for deep-sky observing - no moonlight to wash out faint objects.
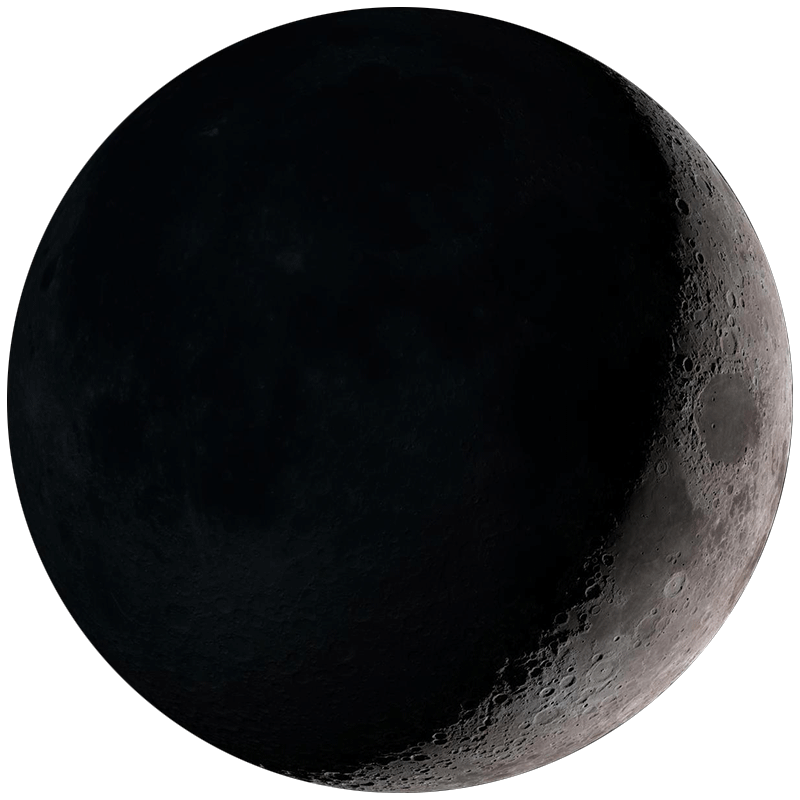

A sliver of light appears on the right side. Visible in the western sky after sunset. Great for observing earthshine on the dark portion.

Half the Moon is lit (right side). High in the sky at sunset, sets around midnight. Excellent for lunar crater observation along the terminator.
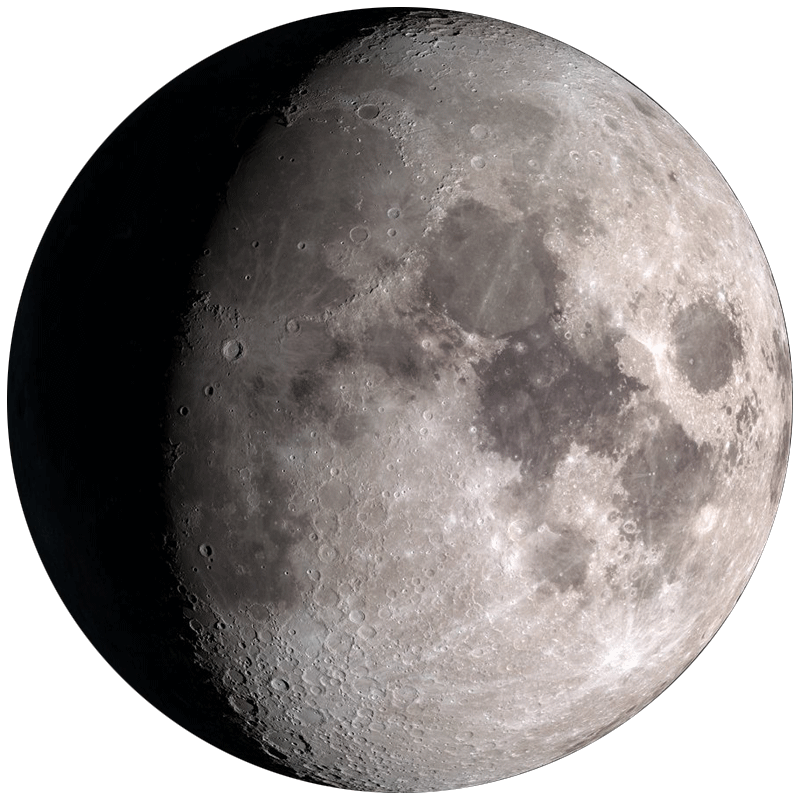
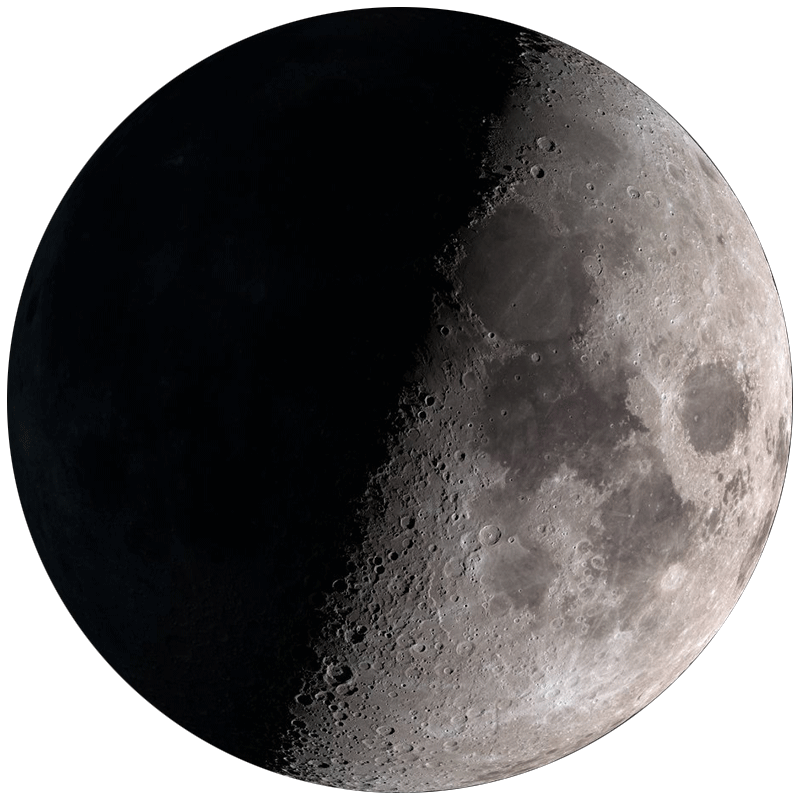
More than half lit, growing toward full. Rises in the afternoon, visible most of the night. Moonlight begins to affect deep-sky viewing.

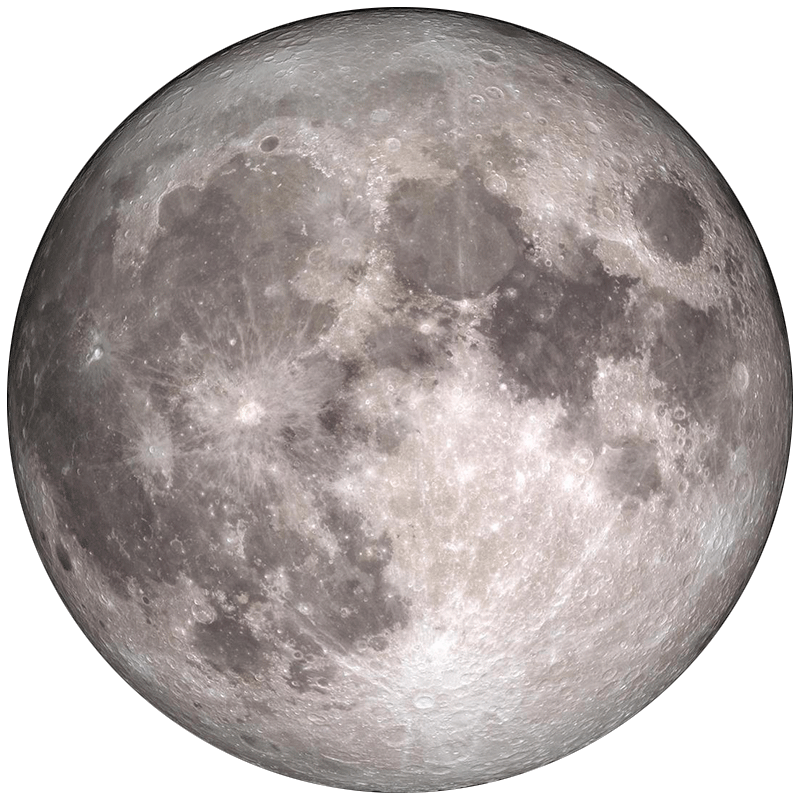
Fully illuminated face visible. Rises at sunset, sets at sunrise. Worst time for deep-sky observing - best for lunar surface features.
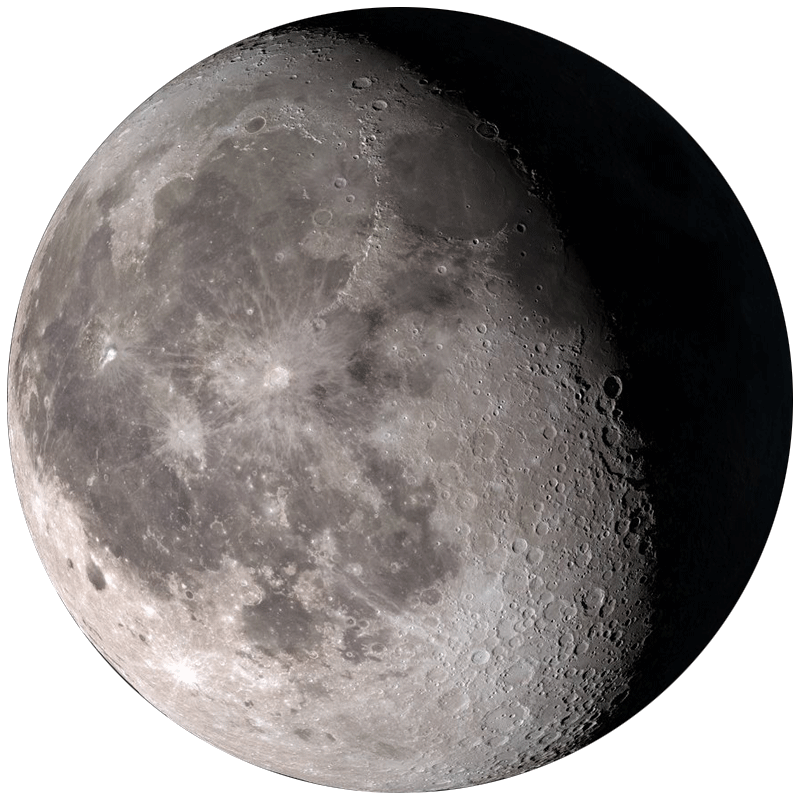

Light decreasing from left side. Rises after sunset, visible in early morning sky. Moonlight still affects late-night observing sessions.

Half the Moon is lit (left side). Rises around midnight, visible in morning sky. Good for early evening deep-sky observation before moonrise.
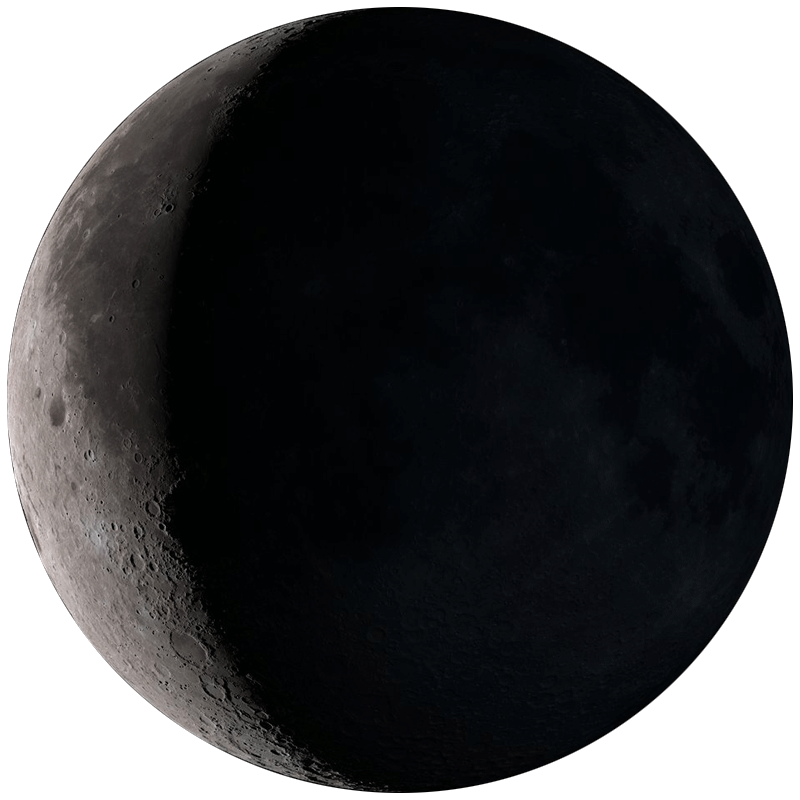

A sliver of light on the left side. Visible in the eastern sky before sunrise. Good for deep-sky observing in the evening hours.
🔭 Lunar Observing Tips
The line between light and dark on the Moon is called the terminator. This is where shadows are longest and crater detail is most dramatic. Best observed during quarter phases.
During crescent phases, you can see the dark part of the Moon faintly lit by sunlight reflected off Earth. This "old Moon in the new Moon's arms" is beautiful in binoculars.
The dark patches on the Moon are ancient lava plains called "maria" (seas). Best seen during gibbous and full phases when lighting is even across the surface.
The Moon can be blindingly bright through a telescope. Use a moon filter or polarizing filter to reduce glare and reveal more surface detail.